European Cross-Border cooperation, known as Interreg A, supports cooperation between regions from at least two different Member States lying directly on the borders or adjacent to them. It aims to tackle common challenges identified jointly in the border regions and to exploit the untapped growth potential in border areas, while enhancing the cooperation process for the purposes of the overall harmonious development of the Union. This article aims to framework the Czech cross-border cooperation programmes that have been lately approved.
The European Commission has adopted a new cross-border programme for the Czech Republic and Poland on September 23rd 2015. This “Interreg” programme covers eight regions on both sides of the border and is worth more than €266 million, with a contribution from the European Regional Development Fund of €226 million. The programme covers different issues:
- The programme puts particular focus on indirect support for employment by tapping into the potential of the tourism sector.
- Despite the fact that tourism constitutes an opportunity for economic development in this mountain area, at present this potential is not exploited enough, mainly due to poor transport infrastructure.
- The programme includes measures aimed at improving the skills of youngsters and eliminating administrative barriers, which hamper their entry into the common labour market, especially regarding the mutual recognition of qualifications. The regions are particularly struggling with a high unemployment rate among young people. The lack of appropriate skills, including linguistic ones, constitutes an obstacle to exploring opportunities linked to a border location.
- The programme will address the issue of risk prevention. An integrated risk management system is envisaged, covering legal, technical, and procedural aspects.
European Commission has also invested more than €90 million to tackle the main cross-border challenges in the Czech-Slovak regions. A key focus will be on cross-border initiatives to boost:
- Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) innovation by increasing cooperation SMEs.
- Strengthen research and promote cooperation between and research institutes and SMEs.
- Protect the environment promoting the sustainable use of the regions’ natural and cultural heritage.
With national funding included the budget of the programme amounts to more than €106 million.
The Czech – Saxony programme cross-border programme was also approved by European Commission lately. The total budget of the programme is EUR 255 million, of which EUR 191.3 million will be provided by the EU Structural Funds. This programme revolves around five priorities and technical assistance measures. Its overall objective is to increase competitiveness and improve living conditions in the border area of Saxony and the Czech Republic.
- Economic development and co-operation between businesses
- Infrastructures
- Environmental and spatial development of the area
- Human resources and networks
- Special support for border regions
- Technical assistance
Interreg V-A – Germany/Bavaria-Czech Republic Cooperation programme also addresses the most important cross-border challenges which are linked to the implementation of the Europe 2020 strategy in the Bavarian-Czech border region. The programme will focus on the following four priorities:
- Strengthen the capacities in research, technological development and innovation
- Conserving and protecting the environment and promoting resource efficiency
- Investment in education
- Sustainable networks and institutional co-operation
The European Commission has adopted too the new cross-border cooperation programme between Austria and the Czech Republic. The programme is worth more than €97 million from EU Regional funds. With national “co-financing” included, it will be worth more than €115 million in investments to tackle the most important cross border obstacles confronting the regions. The programme’s main focus is on
- Environment, conservation, promotion and development of natural and cultural heritage. It will also support projects which aim to protect biodiversity and to test and develop new environmental technologies. Among the results: Better developed and more attractive destinations for sustainable tourism, better protected habitats, increase in eco-innovation applications.
- Human resource development,education and qualification activities increasing human resource potential for local SME.
- Strengthening research, technological development and innovation
- Sustainable networks and institutional cooperation, for better coordination of public services, increased intercultural understanding.
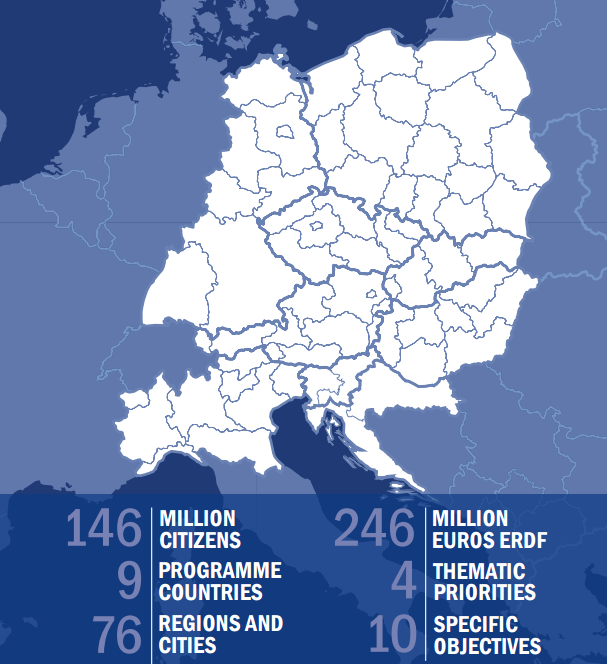
Together with bilateral cooperation policies, Czech Republic is member of Interreg CENTRAL EUROPE programme, a European Union cohesion policy programme, managed by the City of Vienna. Since 2007 the programme has encouraged transnational cooperation among cities and regions of eight central European countries: Austria, the Czech Republic, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Poland, Slovakia, and Slovenia. Croatia now joins the programme as the ninth Member State.
The main investment priorities are:
- Cooperating on innovation to make central Europe more competitive: projects will aim at more effective investment in research, innovation and education and will also address regional disparities in knowledge and education.
- Cooperating on low-carbon strategies in central Europe: projects to increase the use of renewable energies and improving energy efficiency while exploiting opportunity for new jobs in the low-carbon sector.
- Cooperating on natural and cultural resources for sustainable growth in central Europe: projects to help protect and manage natural and cultural heritage, increasingly vulnerable to environmental and economic pressures
- Cooperating on transport to better connect central Europe: projects will aim at improving connections of regions and cities to European transport networks and strengthening multi-modal environmentally friendly passenger and freight transport.
Source: InfoRegio
Article by Nora Lázaro Aguirre